The FAA recently published new standards for vertiport design. (Photo: FAA)
In a recent announcement, the Federal Aviation Administration released new design guidelines for vertiports and vertistops—infrastructure to support electric aircraft that take off and land vertically. The design standards incorporate input from industry partners and the public, and are based on research conducted by the FAA.
The FAA’s Associate Administrator for Airports, Shannetta Griffin, P.E., believes that the U.S. is beginning a new era of aviation. “These vertiport design standards provide the foundation needed to begin safely building infrastructure in this new era,” she remarked in the FAA’s announcement.
The design guidelines cover both public and private vertiports and vertistops that enable electric vertical take-off and landing (eVTOL) aircraft. Additionally, the recommendations listed in the FAA’s associated engineering brief are described as prescriptive and conservative. The FAA notes that the guidance related to vertiport design is likely to evolve in the future to a standard that is performance-based. Therefore, the recently released standards are intended to serve as guidance in the interim.
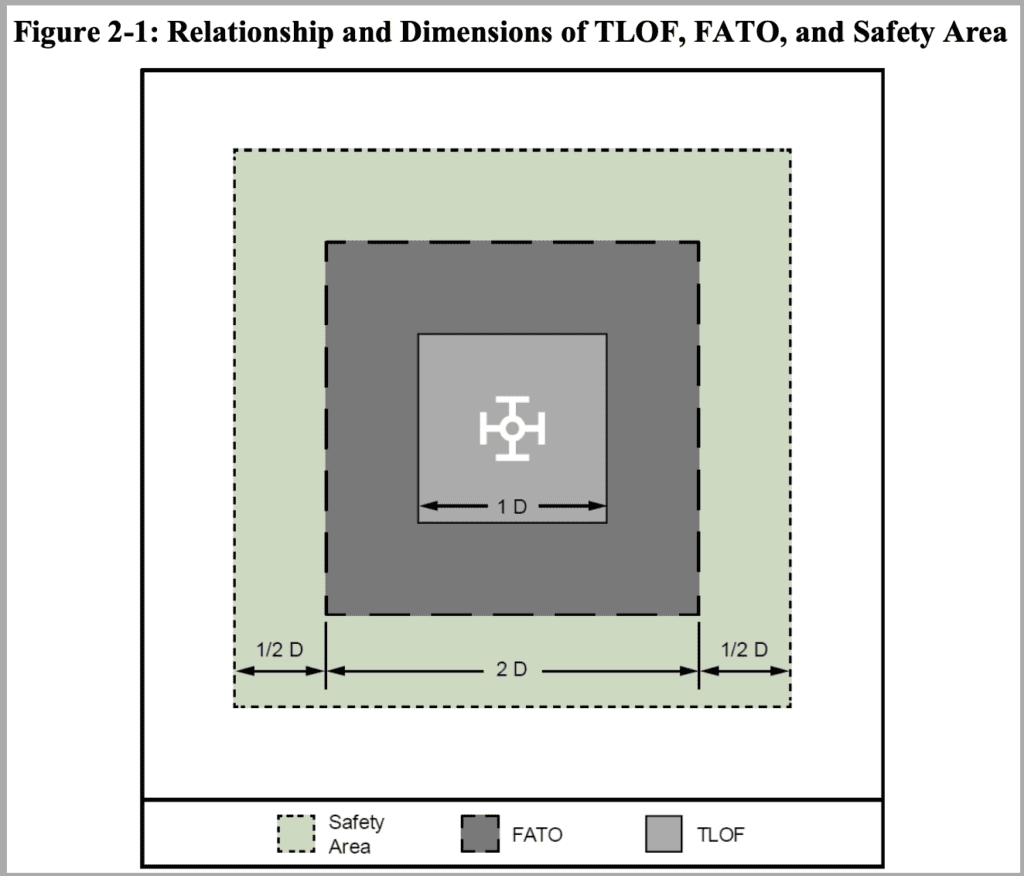
The design standards include recommendations for design and geometry of the area in a vertiport dedicated to take-off and landing. This includes the touchdown and lift-off area (TLOF), the final approach and take-off area (FATO), and the Safety Area which surrounds the FATO.
The TLOF, according to the FAA’s guidelines, should be on level terrain or on a level structure, and it should be centered within the FATO. The design of the FATO should assume dynamic loads of 150% of the eVTOL’s maximum take-off weight. The FATO and the Safety Area should be the same shape as the TLOF (circular, square, or rectangular).
The FAA also makes recommendations for the approach/departure path under visual flight rule (VFR) operations. The preferred paths for the eVTOL’s approach and departure should be aligned with the predominant wind direction whenever possible. Any additional approach and departure paths should, ideally, be separated from the preferred flight path by at least 135 degrees.
Another section of the design standards covers charging and electric vertiport infrastructure for battery-powered aircraft. “Electrification of aviation propulsion systems is an evolving area with few industry-specific standards,” the document states. The FAA recommends that those designing charging infrastructure for vertiports should take into account multiple aircraft-specific systems.
The design guidelines refer to a number of considerations for designing charging infrastructure at vertiports. These include airport/vertiport firefighting and safety considerations, such as the 2021 International Fire Code; Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) considerations, such as for storage and handling of lithium batteries; and power quality considerations, including standards from the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE).

Guidelines for the design of a vertiport at an airport (Photo: FAA)
The FAA also offers a guide for development of vertiport facilities at airports. The agency notes that separate facilities and procedures for eVTOL aircraft may be necessary once the volume of traffic reaches a certain point to affect the operations of other aircraft at the airport.
The TLOF of a vertiport or vertistop built at an airport, according to the FAA, should be located where access to the airport terminal is readily available. For eVTOL aircraft that can perform a conventional take-off and landing on a runway, the TLOF can be built in a location that gives access to fixed-wing aircraft movement areas.
These design guidelines were published by the FAA in late September. ASTM International, the standards development organization, also published a new standard in August that provides guidance to states and municipalities for the design and development of vertiports and vertistops.
Additionally, the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) published “Prototype Technical Design Specifications for Vertiports,” a document offering technical guidance and best practices for urban air mobility infrastructure in Europe. These recommendations were released in March 2022, and EASA expects to publish a Notice of Proposed Amendment in the second half of 2023.